Welcome to A People's Atlas of Nuclear Colorado
To experience the full richness of the Atlas, please view on desktop.
Navigating the Atlas
You may browse the Atlas by following the curated "paths" of information and interpretation provided by the editors. These paths roughly track the movement of radioactive materials from the earth, into weapons or energy sources, and then into unmanageable waste—along with the environmental, social, technical, and ethical ramifications of these processes. In addition to the stages of the production process, you may view in sequence the positivist, technocratic version of this story, or the often hidden or repressed shadow side to the industrial processing of nuclear materials.
Using the buttons on the left, you may also browse the Atlas's artworks and scholarly essays, access geolocated material on a map, and learn more about contributors to the project.
If you would like to contribute materials to the Atlas, please reach out to the editors: Sarah Kanouse (s.kanouse at northeastern.edu) and Shiloh Krupar (srk34 at georgetown.edu).
Cover Image by Shanna Merola, "An Invisible Yet Highly Energetic Form of Light," from Nuclear Winter.
Atlas design by Byse.
Funded by grants from Georgetown University and Northeastern University. Initial release September 2021.
Using the buttons on the left, you may also browse the Atlas's artworks and scholarly essays, access geolocated material on a map, and learn more about contributors to the project.
If you would like to contribute materials to the Atlas, please reach out to the editors: Sarah Kanouse (s.kanouse at northeastern.edu) and Shiloh Krupar (srk34 at georgetown.edu).
Cover Image by Shanna Merola, "An Invisible Yet Highly Energetic Form of Light," from Nuclear Winter.
Atlas design by Byse.
Funded by grants from Georgetown University and Northeastern University. Initial release September 2021.
Abbey Hepner, Monument Plinth: Catalog of 40 uranium disposal cells in the US, 2020, courtesy the artist
Artwork
Uranium disposal cells are geometric mounds engineered to isolate radioactive material from the surrounding environment. The mounds sit above the ground and cover surfaces from a few acres to half a mile, and consist of an outer shell of riprap rock and a clay soil layer that covers the radioactive material. They are designed to allow for rain runoff and to prevent plant growth from forming on top and penetrating the clay layer. Typically, the cells in the Southwest are made from demolished buildings at uranium mines, and the cells in the Midwest and East are most commonly from uranium metal engineering and processing sites.
Some sites that produced the waste contained in the cells date back to the Manhattan Project and were created to mine and construct nuclear weapons; some of the sites continue to operate today for the nuclear energy industry. The amount of radioactivity in the cells varies, but most radiation comes from Uranium-238 with a half-life as old as the earth or 4.47 billion years. There are over 100 sites like these that exist in the U.S. and the number is growing.
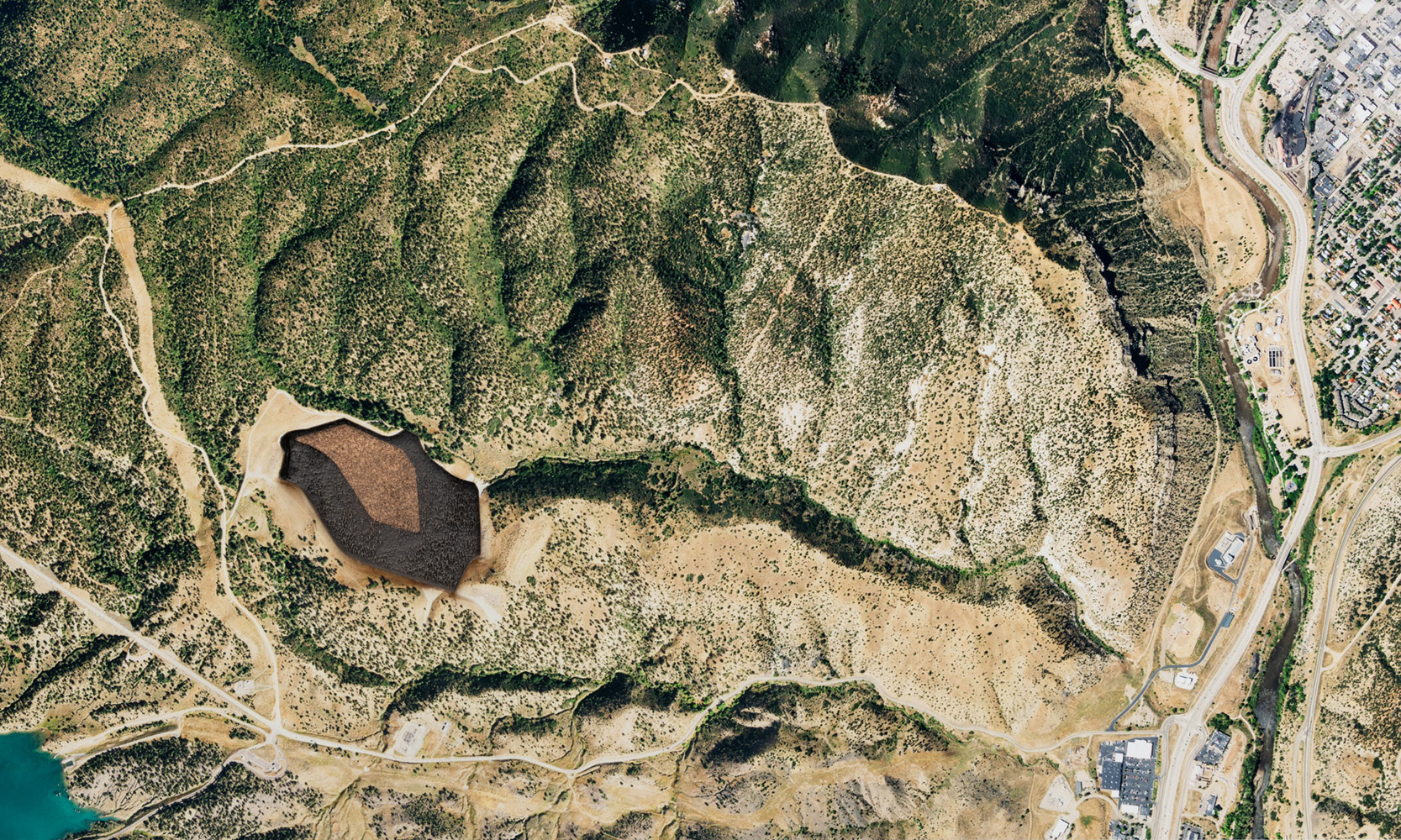

Disposal cells are architecturally fascinating sites. They are often designed to blend in with the landscape, but their shapes form mounds on the earth, and their suture materials seldom remain as invisible as intended. They are otherworldly to see up close, but even more fascinating to see from an aerial view where their odd geometry takes shape. While some sites are constructed away from populated cities, others such as those in Weldon Spring, just outside St. Louis, Missouri, are difficult to ignore and function as recreational destinations.
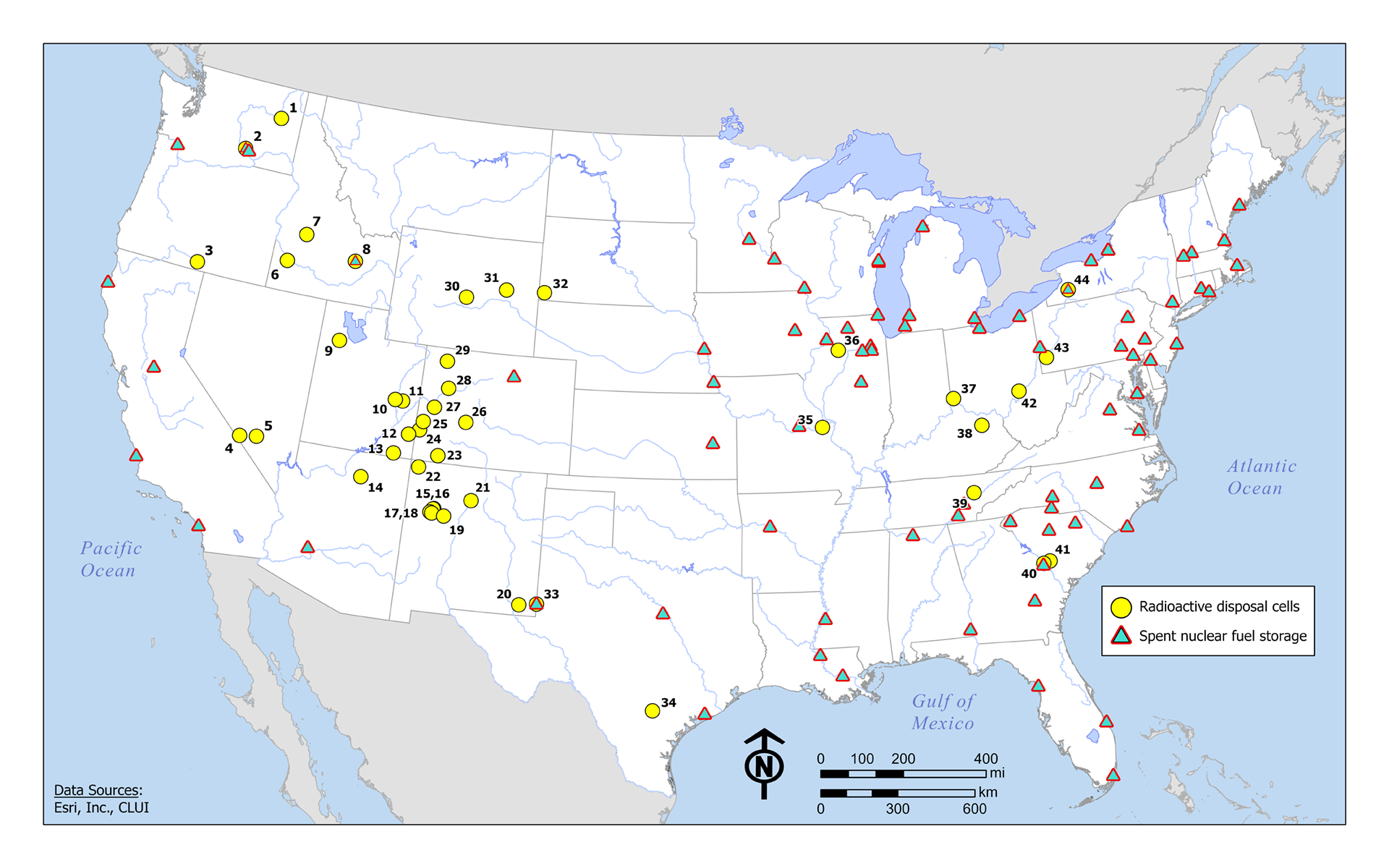
Monument Plinth features aerial images from forty uranium disposal cells across the U.S. The images were collected with the assistance of Dr. Mark Finco and acquired by the National Agriculture Imagery Program. I printed and mounted each image on black acrylic and laser engraved the cell detail into the surface, reflecting an internal space or void.
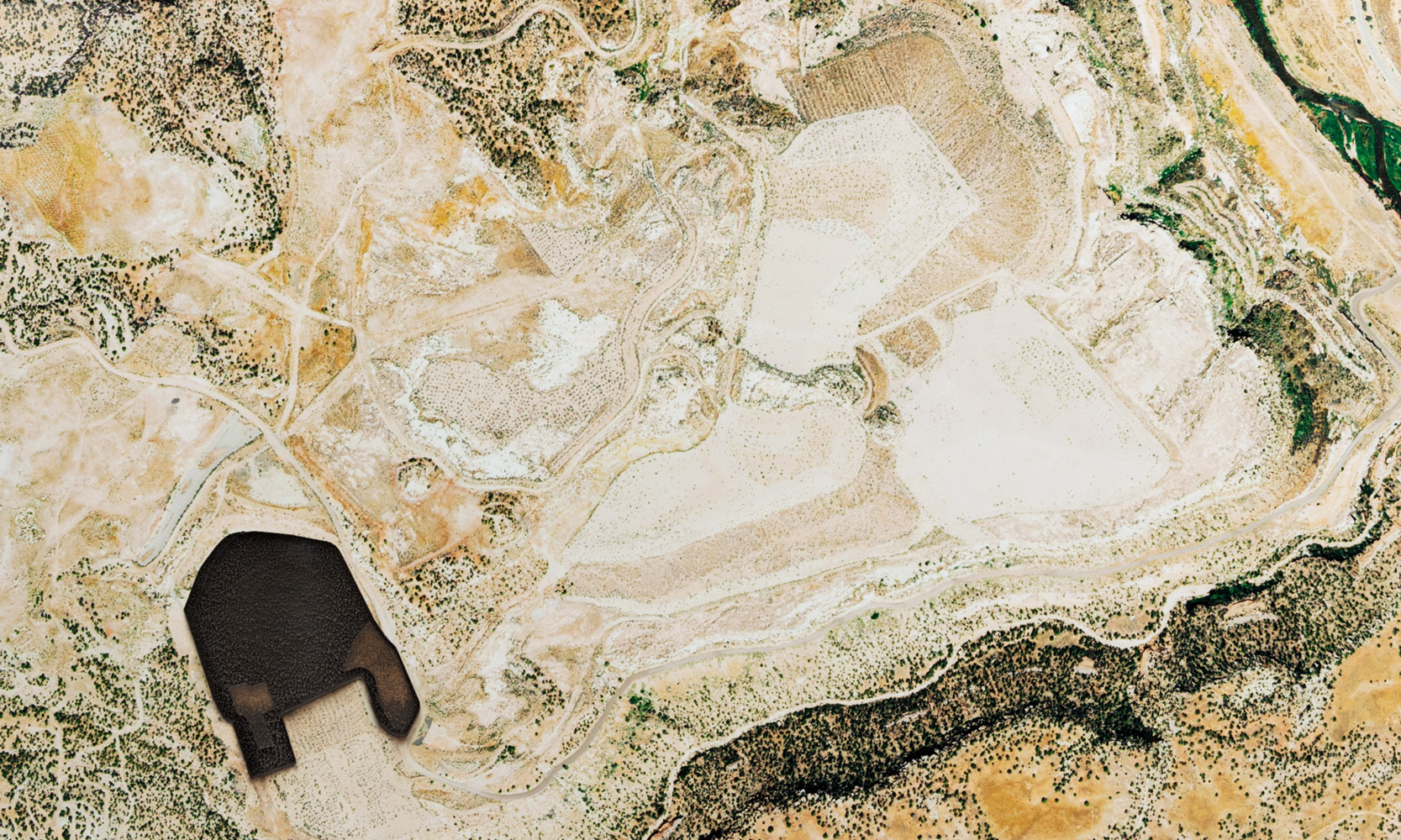

Some sites that produced the waste contained in the cells date back to the Manhattan Project and were created to mine and construct nuclear weapons; some of the sites continue to operate today for the nuclear energy industry. The amount of radioactivity in the cells varies, but most radiation comes from Uranium-238 with a half-life as old as the earth or 4.47 billion years. There are over 100 sites like these that exist in the U.S. and the number is growing.

Abbey Hepner, Monument Plinth: Durango, 2020, courtesy the artist
Disposal cells are architecturally fascinating sites. They are often designed to blend in with the landscape, but their shapes form mounds on the earth, and their suture materials seldom remain as invisible as intended. They are otherworldly to see up close, but even more fascinating to see from an aerial view where their odd geometry takes shape. While some sites are constructed away from populated cities, others such as those in Weldon Spring, just outside St. Louis, Missouri, are difficult to ignore and function as recreational destinations.

Scott White, Monument Plinth: Research Map, courtesy Abbey Hepner
Monument Plinth features aerial images from forty uranium disposal cells across the U.S. The images were collected with the assistance of Dr. Mark Finco and acquired by the National Agriculture Imagery Program. I printed and mounted each image on black acrylic and laser engraved the cell detail into the surface, reflecting an internal space or void.

Abbey Hepner, Monument Plinth: Uravan, 2020, courtesy the artist
Citation
Abbey Hepner, Monument Plinth, laser-engraved archival pigment prints over black acrylic, 20 x 12 inches, ed. 5, 2020.Continue on "Artwork"